|
This section contains 572 words (approx. 2 pages at 300 words per page) |

|
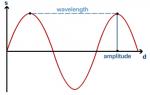
With regard to Earth science, wave motion describes the physical transmission of force or energy potential through a medium of transmission. The transmission disturbs the medium by displacing the medium. For example, water waves propagate through displacement (not linear movement) of water molecules; sound waves propagate via displacement of air molecules. Light also propagates via wave—but not in the same manner as water and sound. Light is transmitted via electromagnetic waves, the alternating of disturbances in electrical and magnetic fields.
A single equation is all that is needed to understand wave motion. The first attempt to mathematically describe wave motion was made by Jean Le Rond d'Alembert in 1747. His equation sought to explain the motion of vibrating strings. While d'Alembert's equation was correct, it was overly simplistic. In 1749, the wave equation was improved upon by Leonhard Euler; he began to apply d'Alembert's theories to all...
|
This section contains 572 words (approx. 2 pages at 300 words per page) |

|