|
This section contains 1,701 words (approx. 6 pages at 300 words per page) |

|
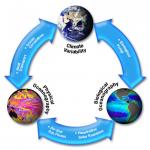
Weather is the state of the atmosphere (mass of air surrounding Earth) at a particular place and point in time. Rain showers, gusty winds, thunderstorms, cloudy skies, droughts (prolonged period of dry weather), snowstorms, and sunshine are all examples of weather conditions. Weather scientists, called meteorologists, use measurable factors like atmospheric pressure (pressure caused by weight of the air), temperature, moisture, clouds, and wind speed to describe the weather. Meteorologists make predictions of future weather based on observations of present regional weather patterns and past trends. Weather prediction, or forecasting, is an important part of meteorology (weather science). Advance warning of such weather phenomena as extreme hot and cold temperatures, heavy rainfall, drought, and severe storms can protect people's property and save lives.
The weather patterns that a region experiences over tens, hundreds, or thousands of years are called climate. For example, the northeastern United States experiences a...
|
This section contains 1,701 words (approx. 6 pages at 300 words per page) |

|