|
This section contains 479 words (approx. 2 pages at 300 words per page) |

|
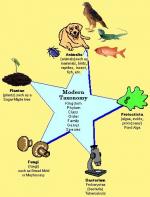
Taxonomy is the naming, describing, and classification of all living organisms and fossils. It is an important part of systematics, the field of biology that deals with the diversity of life. There are three main schools of taxonomy:
- Phenetic taxonomy—which classifies organisms based on overall form and structure or genetic similarity, also called numerical taxonomy;
- Cladistic taxonomy—which classifies organisms strictly based on branching points, focuses on shared, relatively recent (not of ancient origin) characteristics that are common to the species being studied, also called phylogenetic taxonomy; and
- Evolutionary taxonomy—which classifies organisms based on a combination of branching and divergence, also called traditional taxonomy.
Taxonomists collect plants and animals, study them, and group them according to patterns of variation. Taxonomists study plants and animals in nature, laboratories, and museums. Several million species of animals and over 325,000 species of plants are presently known. It is estimated that...
|
This section contains 479 words (approx. 2 pages at 300 words per page) |

|