|
This section contains 796 words (approx. 3 pages at 300 words per page) |

|
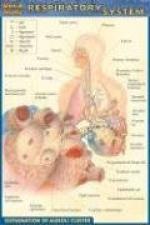
The respiratory system is a series of organs designed to facilitate the exchange of gases, primarily oxygen and carbon dioxide, between red blood cells in the circulatory system and the outside environment. Human cellular physiology requires a constant supply of oxygen (O2) and the ability to ventilate carbon dioxide (CO2) produced as a byproduct of metabolic reactions.
The blood and circulatory system are responsible for the transportation of dissolved or bound gases to and from their principal site of exchange, the lungs. The morphology of the lungs is unique in its deviation from symmetrical bisymmetry. The displacement of the human heart to the left side of the body manifests itself in an unequal division of lobes or morphologically and functionally distinct compartments of lung tissue termed lobes. The heart-side left lung contains two lobes. The right lung normally contains three lobes.
In humans, during normal resting...
|
This section contains 796 words (approx. 3 pages at 300 words per page) |

|