|
This section contains 1,418 words (approx. 5 pages at 300 words per page) |

|
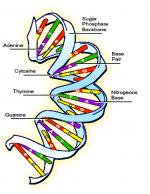
A gene is the fundamental physical and functional unit of heredity. It is an individual element of an organism's genome and determines a trait or characteristic by regulating biochemical structure or metabolic process.
Genes are segments of nucleic acid, consisting of a specific sequence and number of the chemical units of nucleic acids, the nucleotides. In most organisms the nucleic acid is deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) although in retroviruses the genetic material is composed of ribonucleic acid (RNA). Some genes in a cell are active more or less all the time, which means that they are continuously transcribed and provide a constant supply of their protein product. These are the "housekeeping" genes that are always needed for basic cellular reactions. Others may be rendered active or inactive depending on the needs and functions of the organism under particular conditions. The signal that masks or unmasks a gene can come...
|
This section contains 1,418 words (approx. 5 pages at 300 words per page) |

|