|
This section contains 413 words (approx. 2 pages at 300 words per page) |

|
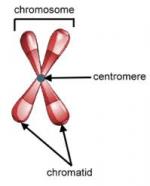
Each pair of chromosomes in the eukaryotic cell contains a unique set of genes and thus the DNA sequence is also unique for each different chromosome pair. When chromosomes are condensed in metaphase, these differences in DNA content produce detectable differences in the staining pattern resulting from exposure to various dyes or stains that interact with the chromatin. The distinctive pattern of bands produced in this manner allows each chromosome pair to be identified and distinguished from all other chromosomes.
Prior to the use of banding methods, chromosomes could be distinguished only by comparing size and the position of the centromere. The first banding method for distinguishing human chromosomes was described by Swedish cytochemist T. O. Caspersson (1910-) in 1969 using the fluorescent dye, quinacrine. This method is called Q-banding. Regions of the genome which are relatively rich in the bases adenine and...
|
This section contains 413 words (approx. 2 pages at 300 words per page) |

|