|
This section contains 873 words (approx. 3 pages at 300 words per page) |

|
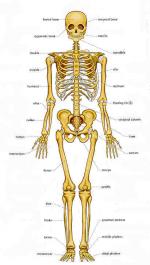
Bone is an organ composed of dense, hard, and flexible connective tissue that makes up the skeletal system of the human body. The extracellular matrix of bone is made up of several components. Protein, collagen in particular, provides bone with its hardness and flexibility. Minerals known as hydroxyapatite are composed primarily of calcium and phosphate with minuscule amounts of magnesium, sodium, potassium, and carbonate and confer hardness in bone. Proteoglycans make up the ground substance in bone and may help to mineralize the osseous tissue. Water is also found in the matrix of bone; some of it is bound to other molecules and some of it is free.
Four types of bone cells help to form and maintain the extracellular matrix of bone. The first type is unspecialized cells, called osteoprogenitor cells that eventually differentiate into osteoblasts and other connective tissue. Osteoblasts are the second type...
|
This section contains 873 words (approx. 3 pages at 300 words per page) |

|