|
This section contains 889 words (approx. 3 pages at 300 words per page) |

|
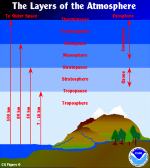
Atmosphere refers to the mixture of gases and suspended particles surrounding a celestial object that has a gravitational field strong enough to prevent the gases and particles from escaping. The atmosphere of the earth is composed almost entirely of oxygen and nitrogen in their diatomic forms, i.e., as two atoms bound together by chemical bonds. Nitrogen gas (N2) accounts for approximately 78% of the atmosphere, while oxygen (O2) represents nearly 21%. In the remaining 1%, the inert noble gas argon makes up about 0.9% and carbon dioxide (CO2) about 0.03%. The rest is composed of trace gases, including carbon monoxide, water vapor, hydrogen, methane, neon, helium, krypton, xenon, and ozone. The relative concentrations of these gases varies with their distance from the earth's surface.
Oxygen is required for the respiration of air-breathing animals and to burn organic materials. Carbon dioxide, though present in small amounts, maintains the heat balance of the earth...
|
This section contains 889 words (approx. 3 pages at 300 words per page) |

|