|
This section contains 882 words (approx. 3 pages at 300 words per page) |

|
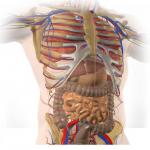
Anatomy is the study of the structure of living things. There are three main areas of anatomy: cytology studies the structure of cell; histology examines the structure of tissues; and gross anatomy deals with organs and organ groupings called systems. Comparative anatomy, which strives to identify general structural patterns in families of plants and animals, provided the basis for the classification of species. Human anatomy is a crucial element of the medical curriculum.
Modern anatomy, as a branch of Western science, was founded by the Flemish scientist Andreas Vesalius, who in 1543 published De Humani Corporis Fabrica (Structure of the human body), one of the great works in the history of science. In addition to correcting numerous misconceptions about the human body, Vesalius's book was the first description of human anatomy that organized the organs into systems. Although initially rejected by many followers of classical anatomical doctrines, Vesalius's systematic...
|
This section contains 882 words (approx. 3 pages at 300 words per page) |

|