|
This section contains 603 words (approx. 3 pages at 300 words per page) |

|
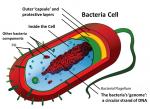
Bacterial Transformation
Bacterial transformation is what happens when a
bacterial cell accepts outside DNA and incorporates it
into its own DNA. This generally occurs within
plasmids, (small circular DNA molecules apart from
chromosomes). There's between 10 and 200 copies of the
same plasmid in a cell. Plasmids can reproduce when
the chromosome does, or independently. Each plasmid
has between 1,000 and 200,000 base pairs. Specific
plasmids, called R plasmids, carry genes for
resistance to antibiotics like ampicillin (used in the
lab).
Plasmids role in transformation is two things. They
transfer genes that take place naturally within the
plasmid, or they act as vectors for incorporating
outside DNA. Restriction enzymes are used to cut
outside DNA and insert it into the plasmid. The
bacteria used in this lab was E. coli. It was chosen
because it can be grown without difficulty in Luria
broth or on agar.
Hypothesis:
The transformed E. coli with the...
|
This section contains 603 words (approx. 3 pages at 300 words per page) |

|