|
This section contains 861 words (approx. 3 pages at 300 words per page) |

|
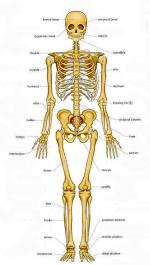
Bone is the major component of the adult vertebrate skeleton. It is a hard connective tissue comprised of living material, including bone cells, fat cells, and blood vessels, and an inorganic matrix, which is made up largely of water and minerals.
All connective tissues support and connect various parts of the body, and the specific functions of bones are diverse. As the main element of the skeleton, they provide structure and support to vertebrate bodies. They also act as levers for body movement, their position controlled by the muscles attached to them. Bones also protect the delicate internal organs from external impact. For example, the skull encases and protects the brain, and the rib cage houses the lungs and heart.
As well as serving these structural and protective functions, bones play two important physiological roles. They serve as deposits for calcium, a mineral that makes the bones stronger...
|
This section contains 861 words (approx. 3 pages at 300 words per page) |

|